RavenDB
Author: Aleksander Klevjer <aklevjer>Introduction
RavenDB is an open-source NoSQL document database designed for scalable data storage and retrieval. Since its release in 2010, it has gained traction among developers for its ease of use and flexibility. Commonly used in web development, the Internet of Things (IoT), and enterprise solutions, RavenDB is known for its ability to manage large volumes of data while ensuring reliability. It offers both cloud-hosted and self-hosted deployment options, making it suitable for various environments.
Brief History
- 2008: Originally named “Rhino DivanDB,” RavenDB was created by Oren Eini.
- 2009: Development begins to create a fully-featured document database.
- 2010: RavenDB is launched as the first document database on the .NET platform.
- 2015: RavenDB reaches 1 million downloads.
- 2016: New clustering capabilities are introduced, along with better integration tools.
- 2017: RavenDB surpasses 2 million downloads.
- 2018: Raven Query Language is introduced, and performance improvements are made.
- 2019: RavenDB Cloud is launched, offering DBaaS on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- 2020: Cloud storage costs are reduced by 50%, and IoT application support is enhanced.
- 2023: Features for handling larger databases and a new search engine are introduced.
Main Features
RavenDB is a document database solution that offers various features for managing data efficiently. The following sections outline these key functionalities, addressing common data management challenges.
Cloud Support
RavenDB Cloud offers Database as a Service (DBaaS) capabilities, allowing developers to deploy databases across cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This simplifies backend management and reduces operational costs while supporting scalability.
Real-Time Data
With real-time data capabilities, RavenDB allows developers to receive live updates as data changes occur. This can be particularly beneficial for applications such as messaging platforms, where new messages are instantly delivered to users without the need for a page refresh.
Scalability
RavenDB supports horizontal scaling through sharding, a method of distributing data across multiple servers. This means that as an application grows in terms of data size or traffic, more servers can be added to handle the increasing load, ensuring performance remains optimal. This allows RavenDB to support large applications with growing traffic.
High Availability
With built-in clustering and replication, RavenDB offers high availability and reliability. Clustering allows multiple servers to function as a single system, distributing the load and providing fault tolerance. Replication copies data across servers, ensuring that if one server fails, another can take over, allowing seamless data access even during outages.
Performance Optimization
RavenDB includes advanced indexing features designed to improve query performance and efficiency, resulting in faster data retrieval. Indexing speeds up data searches by creating a structure that allows the database to locate information more quickly. This is particularly beneficial for applications with large amounts of data, as it significantly reduces search times and enhances overall performance.
Document-Oriented Storage
RavenDB uses a document-oriented data model, allowing developers to store data in JSON format. Each document contains all relevant information about an object, which simplifies retrieval and updates. Unlike traditional databases that separate data across multiple tables, this model consolidates everything in one place, streamlining development and improving performance.
ACID Compliance
RavenDB is ACID-compliant, meaning it adheres to four key principles: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. This ensures that all transactions are processed reliably, so data remains accurate and intact, even in the event of failures. ACID compliance is crucial for maintaining data integrity and reliability in applications.
Querying with RQL
The Raven Query Language (RQL) is a SQL-like language for querying JSON-based documents in RavenDB. It uses a familiar syntax that helps developers transition from SQL databases. Additionally, it allows for efficient querying, filtering, and management of complex nested data structures.
Example RQL Query:
from Userswhere Age > 18select Name, EmailThe above query retrieves the names and email addresses of users older than 18 years, demonstrating how RQL can be used for data retrieval.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
-
Ease of Use: RavenDB’s intuitive interface and automatic indexing simplify database management, making it easy for teams without deep database expertise to get started quickly.
-
Scalability: Through sharding, RavenDB supports horizontal scaling, making it suitable for businesses with growing traffic, such as e-commerce and Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms.
-
Performance: With its advanced indexing features, RavenDB can support data-heavy applications like real-time analytics that require fast response times.
-
Document Store: RavenDB’s JSON-based document model simplifies data management, making it easier to adapt to changing requirements without major restructuring.
-
ACID Transactions: RavenDB supports ACID transactions across multiple documents, ensuring data consistency and integrity, which is critical for apps like financial systems and e-commerce.
Weaknesses
-
Resource Intensive: RavenDB may require more memory and CPU, especially with large datasets, which could lead to higher infrastructure costs.
-
Advanced Complexity: While easy for basic use, RavenDB’s advanced features like custom indexing and sharding can be complex, requiring more expertise for optimization.
-
License Cost: Although the Community Edition is free, advanced features in the Professional and Enterprise editions can be expensive for larger teams.
-
Smaller Ecosystem: Compared to competitors like MongoDB, RavenDB’s ecosystem is smaller, which may limit available plugins, integrations, and community support.
-
Data Duplication: The document model may lead to data duplication, especially in scenarios with highly relational data, which can increase storage needs.
Market Comparison
As a NoSQL database, RavenDB competes with other popular solutions like MongoDB and Couchbase. While these systems offer similar functionalities, each has unique strengths and weaknesses that make them suitable for different applications.
Comparison Table
| Factor | RavenDB | MongoDB | Couchbase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Document Model | Rich document support | Flexible schema | Document + key-value model |
| Ease of Use | Easy for basic use, more complex for advanced features | Easy to start, complexity increases at larger scale | Easy to use, setup can be more complex |
| Performance | High - optimized for read and write operations | High - Excellent performance for read-heavy workloads | High - Fast reads and writes, with built-in caching |
| Scalability | Horizontal scaling through configurable sharding | Horizontal scaling with built-in sharding | Horizontal scaling with automatic sharding |
| Ecosystem & Support | Smaller ecosystem, active community | Large ecosystem, many integrations | Strong support, smaller community |
| Use Cases | IoT, e-commerce, enterprise applications, real-time analytics | Content management systems, social media, big data analytics | Mobile applications, gaming, financial services |
Key Differences
-
Document Model: All three databases use a document-based approach. Couchbase combines document storage with key-value capabilities to speed up access to frequently requested data. MongoDB offers a flexible schema that supports various data types, while RavenDB prioritizes data consistency and structure.
-
Ease of Use: RavenDB is designed for straightforward initial setup and basic usage, but can become more complex with advanced features. MongoDB is easy to start with, but may require a deeper understanding as applications scale. Couchbase is user-friendly for basic tasks, but its setup can be more intricate at larger scales.
-
Performance: RavenDB’s indexing system is optimized for both read and write operations, making it ideal for data-heavy applications. MongoDB is specifically optimized for read-heavy workloads, while Couchbase enhances performance through built-in caching, benefiting applications that require frequent read requests and real-time data access.
-
Scalability: All three databases support horizontal scaling. MongoDB may require more complex configurations at larger scales. Couchbase automates sharding for easier management, while RavenDB provides a simpler approach with customizable sharding options.
-
Ecosystem & Support: MongoDB features a larger ecosystem with extensive community support and resources. Couchbase offers strong support for mobile and gaming applications, whereas RavenDB has a smaller yet active community.
-
Use Cases: RavenDB is well-suited for applications requiring strict data consistency, such as e-commerce and IoT. MongoDB’s flexibility benefits adaptable applications like CMS and social media platforms, while Couchbase is often chosen for mobile and gaming applications where quick access to cached data is essential.
Getting Started
RavenDB supports multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This guide will walk you through the process of getting started on Windows.
- Download RavenDB:
- Download the latest stable version from RavenDB website.
- Extract and Run:
- Extract the zip file into a folder of your choice.
- Run
Raven.Server.exeto start the server.
- Access the Setup Wizard:
- Once the server is running, note the message in the command prompt that indicates the server’s URL, such as:
Server available on: http://127.0.0.1:8080
- Open this URL in your browser to access the RavenDB Setup Wizard.
- Once the server is running, note the message in the command prompt that indicates the server’s URL, such as:
- Complete the Setup Wizard:
- Follow the steps in the RavenDB Setup Wizard.
- For local testing, select the Unsecure option, which doesn’t require a license key (suitable for development only).
- For production use, choose the Secure option, which requires registration and a license key.
- Access RavenDB Studio:
- After completing the setup, click the Restart Server button to apply the settings. The server will then redirect you to RavenDB Studio, where you can manage and interact with your database through its web interface.
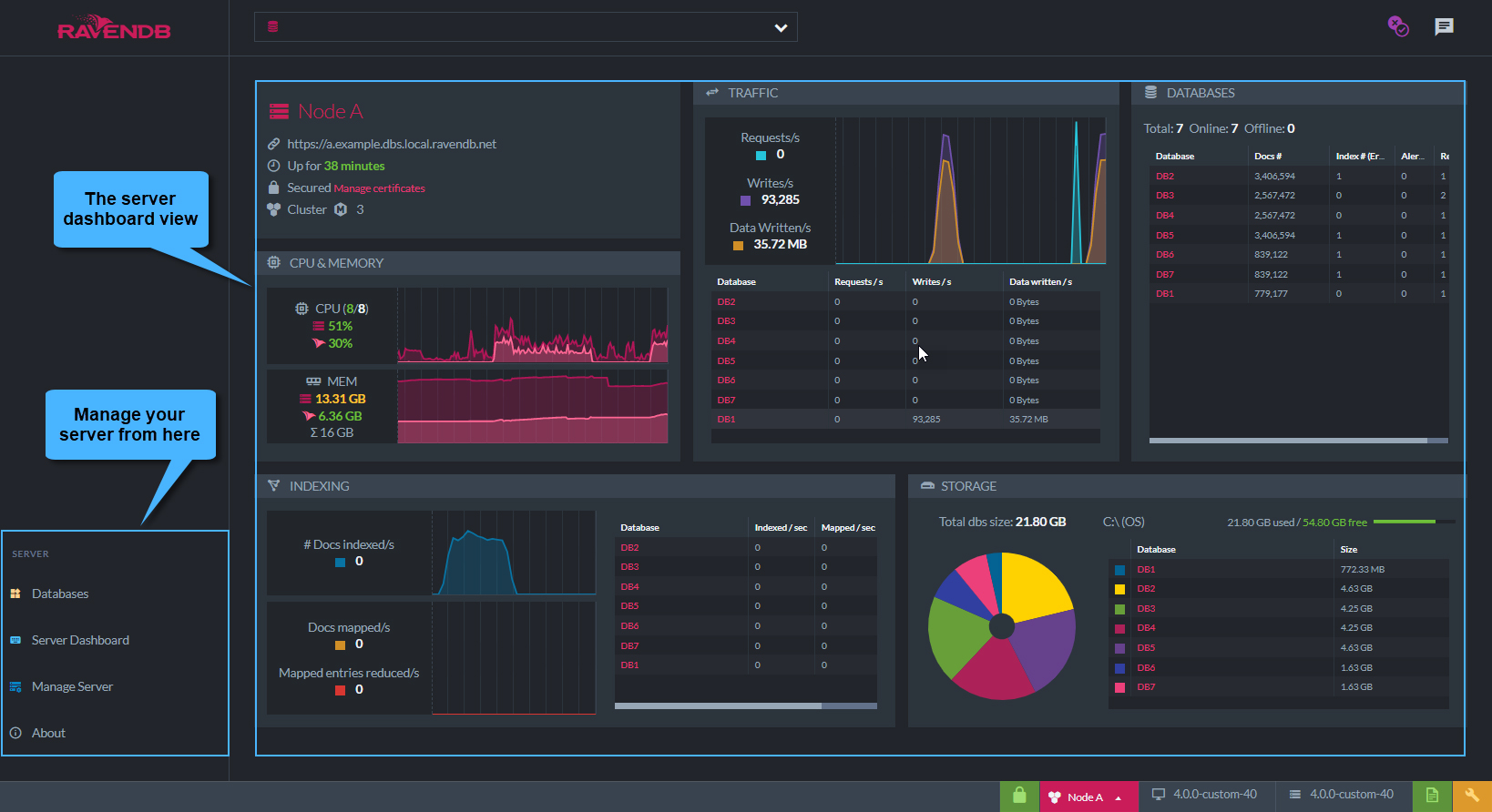 Overview of RavenDB Studio interface.
Overview of RavenDB Studio interface.
Conclusion
RavenDB is a NoSQL document database that emphasizes data consistency and integrity. With features like advanced indexing and ACID compliance, it’s well-suited for applications such as e-commerce, IoT, and enterprise solutions, where managing large volumes of data while ensuring reliability is essential.
However, users may face challenges due to the complexity of its advanced features and a smaller ecosystem compared to larger competitors. Despite this, RavenDB remains a competitive option for developers looking for efficient data handling and scalability in their applications.
References
- RavenDB: Features
- RavenDB: Roadmap
- RavenDB: Inside RavenDB
- DB-Engines: RavenDB vs MongoDB vs Couchbase
- BairesDev: Comparison of Popular NoSQL Databases
- freeCodeCamp: How to Create a NoSQL Database with RavenDB