Travis-CI Case Study
Author: Morten Ramfjord, RamsnesIntroduction
Travis-CI is a hosted, open sourced continuous integration (CI) platform. Developers’ software builds, tests, deployments and infrastructures are set up and managed by Travis-CI.
Brief History and platform information
Travis CI, established in 2011, was founded in Germany, Berlin. It quickly became a trusted name in the continuous integration- and deployment world among engineers and developers.
In 2019, Idera, Inc. acquires Travis CI for their CI capabilities. Travis CI then joined Idera’s testing division.
Travis CI has some impressive statistics as a developer platform. They have:
- Over 700.000 active users
- Over 60.000 active projects every day
- 2.5 million build minutes every day
- Almost 1 million active open source projects
- Over 300.000 active projects use Travis CI
Main Features
The primary purpose of Travis CI is to help test and deploy developers’ software builds. Utilizing Travis CI’s service and their tools makes the process more reliable and less time-consuming for the client, thus improving the development process.
Features
- Automated Build and Testing:
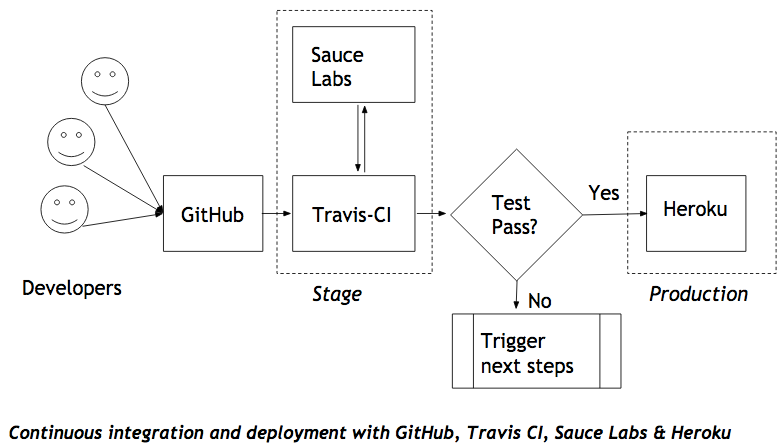
- Trigger Builds: Automatically launch builds upon code pushes, ensuring immediate feedback and updates, as seen in the “Stage” section in the image at the end of this section.
- Parallel Testing: Run tests concurrently for faster build times and efficient resource utilization and delegation.
- Caching: Reduce unwanted rebuilds by caching tested dependencies- and build artifacts.
- Support for Diverse Languages and Frameworks achieves: Seamless integration with a variety of languages, like Python, Ruby, Java, JavaScript, and frameworks like Django, Rails, Spring Boot, and React.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD):
- Environments and Stages: Define build stages (build, test, deploy) and configure separate environments for development, staging, and production.
- Deployment Integration: Utilize built-in integrations with deployment platforms like Heroku, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform for automated deployments.
- Rollbacks and Recovery: Implement rollback mechanisms to revert to previous versions in case of issues.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- Flexible Configuration: Adapt Travis CI to your project with custom scripts, plugins, and environment variables.
- Parallel Builds: Run multiple builds concurrently for large projects or complex testing scenarios.
- Multiple Execution Platforms: Execute builds on Linux, macOS, and Windows platforms for optimal compatibility.
- Collaboration and Visibility:
- Notifications: Stay informed about build progress and results through email, Slack, or other notification channels.
- Detailed Reporting: Generate comprehensive reports and visualize build history with dashboards and charts.
- Team Management: Assign roles and permissions within your Travis CI organization for efficient collaboration and control.
- Security and Reliability:
- Secrets Management: Securely store sensitive data like passwords and API keys, preventing accidental exposure.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Integrate vulnerability scanners to identify and address security issues in your codebase.
- Audit Logs: Track build execution history and monitor activities for improved security and accountability.
- High Availability: Built on a robust infrastructure for reliable and consistent performance.
- Open Source Integration:
- Free Plans: Open-source projects can leverage Travis CI’s functionality for free, making it accessible to all developers.
- Extensive Integrations: Connect with countless tools and services you already use in your development workflow.
- Active Community: Benefit from a vibrant community of developers and contribute to the platform’s open-source codebase.
How Travis CI works and Architecture (www.devopsschool.com)
Applications
Software development tools utilized
Ruby on Rails, Ember.js, OpenSSL, Puppet and Logstash.
These are all software development tools that address different parts of the development process:
- Ruby on Rails: A full-stack web application framework. It is a popular choice for web development because it provides a lot of functionality out of the box.
- Ember.js: A JavaScript framework, known for its ease of use and its ability to create complex UIs.
- OpenSSL: A toolkit that implements a variety of cryptographic functions and protocols. It is used for a wide range of security purposes, including encrypting communications, verifying digital signatures, and authenticating users.
- Puppet: A infrastructure automation tool. It allows you to automate the configuration and management of computer systems. Puppet is a popular choice for managing large deployments of servers.
- Logstash: A data processing pipeline. It allows you to collect data from a variety of sources, transform it into a common format, and then send it to a central repository for analysis.
Testing tools utilized
The testing tools included from Ideras division are:
TestRail, Ranorex, and Kiuwan. They focus on different aspects of the testing process:
-
TestRail: A test case management tool. It helps testers create, manage, and track test cases. This can include things like writing test steps, assigning tests to testers, and tracking the results of tests.
-
Ranorex: A test automation tool. It allows testers to automate repetitive testing tasks. This can save a lot of time and help to ensure that tests are run consistently.
-
Kiuwan: An application security testing tool. It helps developers identify and fix security vulnerabilities in their code - important for ensuring that software is safe to use.
Market Comparison
There are many CI-tools at disposal in the market. A comparisation of Travis CI to Jenkins- and Circle CI:
Travis CI vs. Jenkins vs. Circle CI
| Travis CI | Jenkins | CircleCI |
|---|---|---|
| Simple setup configurability | Complex configurability | Advanced configurability and setup time |
| Ease of use | Extensibility | Flexible cloud terms |
| User-friendly interface | Advanced interface | Flexible deployment options |
| Accessable learning curve | Steep learning curve | Wider range of third party choices |
Platforms utilized
| Travis CI | Jenkins | CircleCI |
|---|---|---|
| Heroku, GitHub Pages, and AWS S3 | Windows, Linux, macOS and miscellaneous Unix-like OS’ | AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, Slack, GitHub, and Jira |
In short, the different profiled platforms comparable to TravisCI has the following strenghts that separates them:
- Travis CI is a good option for those getting started with CI/CD, especially for open-source projects on GitHub.
- Jenkins is ideal for complex setups and customization but requires more configuration effort.
- CircleCI offers a balance between ease of use and flexibility, with good cloud support and third-party integrations.
Getting Started with Travis CI using GitHub
- Sign up and begin your connection
- Visit the website and familiarise yourself
https://www.travis-ci.com/- Sign in to your active GitHub account
https://app.travis-ci.com/signin-
Choose what build-repository you would like to test
-
Click “Authorize Travis CI” to grant access to your repositories
-
Select “Activate” on the desired repository on your Travis CI dashboard
- Configure .travis.yml-file
- the .travis.yml-file instructs Travis CI how to act during a build The following example is a Ruby project built with version 2.2: .travis.yml:
language: rubyrvm: - 2.2 - jruby-
Add the .travis.yml file to git, commit, and push to trigger a Travis CI build:
git commit -m "Message"git push origin <<branch-name>>Note: Travis CI needs to have a .travis.yml-file commited to run.
-
Give access to Travis CI when prompted after sign-in via GitHub This will give the prompt: “This application will be able to read and write all public and private repository data.”
Note: For use of Travis CI via other options than GitHub, or changing programming language visit: https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/tutorial/
Conclusion
Travis-CI offers a robust and user-friendly CI platform, especially for open-source projects. Its extensive features and ease of use make it a valuable tool for developers of all experience levels. By integrating with various programming languages, frameworks, and deployment platforms, Travis-CI streamlines the development process, reduces manual work, and ultimately improves software quality. While there are other CI tools available, as mentioned in the comparison section, Travis-CI stands out for its focus on simplicity and ease-of-use. If one is looking for a reliable and efficient way to automate your software builds and deployments, Travis-CI is a strong candidate to consider.